Neuropathy 101: Vital Information into Nervous System Function
Neuropathy is a malady that affects the sensitive system of neural pathways that communicate signals between the central nervous system and the other of the physical form. It can present itself in diverse forms, impacting everything from feeling to motor function. Understanding neuropathy is important not just for those affected with it, but for everybody seeking to maintain nerve health and enhance holistic health.
As we explore into the realm of neuropathy, it becomes evident that this condition can arise from numerous causes, including diabetic conditions, physical injury, pathogens, and even particular drugs. The indications can vary widely, but many people report sensations such as pins and needles, burning, or insensitivity in their arms and legs. By gaining new promise neuropathy of neuropathy, we can enhance our appreciation for the vital function our nerves play in our daily lives and identify ways to support better nerve function.
Grasping Neuropathy
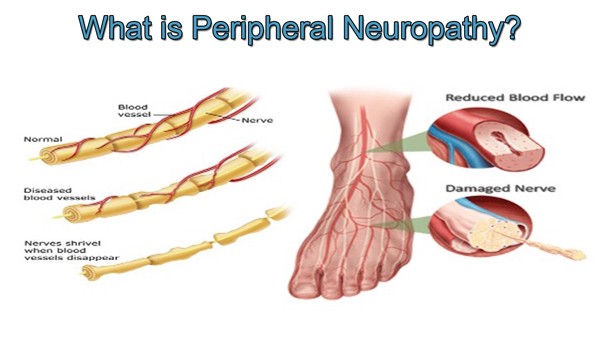
Peripheral neuropathy is a phrase that denotes a range of conditions affecting the peripheral nervous system, which associates the cerebrum and spinal cord to the other parts of the body. This situation can arise due to multiple causes, including diabetes, inflammatory diseases, trauma, and exposure to toxins. Neuropathy can cause signs such as discomfort, tingling, numbness, and reduced strength, often impacting the hands and feet.
The consequences of this condition can be considerable, impacting daily activities and overall life quality. Individuals may encounter difficulty with balance and motor skills, rendering routine tasks more difficult. In cases of severe neuropathy, it can lead to issues such as skin sores or infectious diseases due to the decrease of feeling and protective reflexes in affected areas.
Diagnosis of this condition includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and sometimes specialized tests like nerve testing or blood tests. Timely identification and treatment are essential in stopping further nerve damage and relieving the condition. Treatment options can be diverse, aiming at treating root causes, alleviating discomfort, and enhancing nerve function.
Origins and Risk Factors
Nerve damage can arise from a variety of sources, with the most common being diabetes. Diabetic neuropathy occurs when elevated blood glucose damage the nerve fibers over time, particularly in the legs and feet. Such neuropathy affects a large number of individuals with the condition and is a leading cause of ulcerations of the feet and amputations. Other metabolic disorders, such as low thyroid function and hepatic issues, can also play a role to nerve damage.
In furthermore to metabolic conditions, contact to toxins and certain medications can lead to neuropathy. Common culprits include heavy metals like plumbum and Hg, as well as drugs employed in cancer treatment. Excessive alcohol consumption is another risk factor since high alcohol intake can result in nutrient deficiencies that harm the health of the nerves. Environmental toxins, found in certain job sites or residences, may also pose risks for nerve damage.
Genetics and inherited conditions play a significant role in the probability of contracting nerve damage. Conditions such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease are examples of genetic nerve disorders that impact the functioning of nerves. Furthermore, factors such as aging, living habits, and general health can increase the risk of nerve damage. For instance, older adults are more prone to neuropathy due to a natural decline in the functioning of nerves and health over time.
Administration and Care Alternatives
Optimal administration of neuropathic conditions involves a multi-faceted approach customized to the underlying issue and the specific signs experienced by the person. Drug therapies play a crucial role in mitigating pain associated with nerve pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as paracetamol or Advil may provide relief for light discomfort. However, those with acute cases may benefit from pharmaceutical medications, including seizure medications or antidepressants, which can help to alter nerve pain responses.
In addition to drug treatments, daily life modifications are important for controlling neuropathy. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and compounds, particularly B complex vitamins, can support nerve health. Routine exercise can also enhance circulation and alleviate symptoms. Movement therapy may be advised to enhance mobility and power, thereby tackling any physical limitations caused by neuropathic conditions. Furthermore, eliminating toxins such as intoxicants and certain medications known to affect nerve health is imperative.
Additional therapies may also be investigated as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Methods such as needle therapy, massage, and biofeedback have proven potential in relieving neuropathic pain for some patients. Additionally, supplements like alpha-lipoic acid or omega-3 fatty acids may provide benefits in managing symptoms. Working closely with health practitioners ensures that people receive tailored and efficient interventions tailored to their unique cases with neuropathic conditions.